The Procedure
Are There Any Alternatives to an Oophorectomy?
Pain is usually controlled with painkillers or by using hormone treatment such as the oral contraceptive pill.
If you have not yet gone through menopause, small cysts can usually be safely left alone.
What Does the Oophorectomy Involve?
The operation is usually performed under a general anaesthetic and usually takes about 30 minutes.
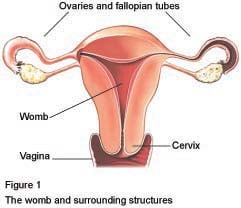
Your gynaecologist will make several small cuts on your abdomen. They will insert surgical instruments, along with a telescope, inside your abdomen and perform the operation.
Your gynaecologist will separate your ovary and remove it. They may need to place instruments through your vagina to help them remove your ovary.
What Complications Can Happen?
General Complications
- Pain
- Feeling or being sick
- Bleeding
- Infection of the surgical site (wound)
- Unsightly scarring
- Blood clots
Specific Complications of This Operation
- Damage to structures such as your bowel, bladder or blood vessels
- Developing a hernia near one of the cuts
- Surgical emphysema
- Ovarian remnant syndrome
- Damage to a ureter